How Many Wires For Ac Underground Service
by Nick Gromicko, CMI® and Kenton Shepard
Poorly installed and maintained electric cables are a common cause of electrical fires in homes. Many older homes incorporate wiring that is now considered obsolete or dangerous. InterNACHI inspectors should sympathise the basic distinctions between the dissimilar types of cable systems and so that they can place unsafe conditions.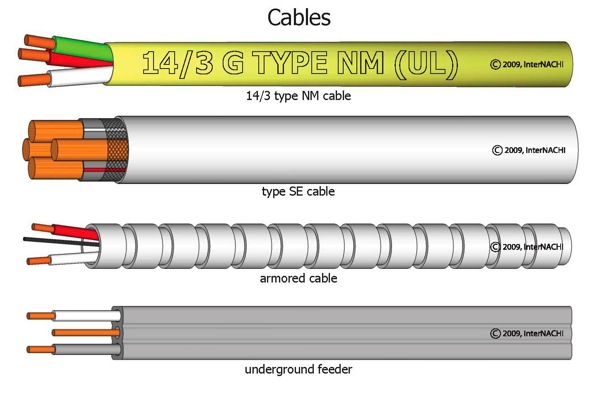
Romex Cables
Romex is the merchandise name for a blazon of electrical conductor with non-metal sheathing that is unremarkably used as residential branch wiring. The following are a few bones facts about Romex wiring:
- Romex™ is a common type of residential wiring that is categorized past the National Electrical Code (NEC) as underground feeder (UF) or not-metallic sheathed cablevision (NM and NMC).
- NM and NMC conductors are composed of ii or more than insulated conductors contained in a not-metallic sheath. The coating on NMC cable is non-conducting, flame-resistant and moisture-resistant. Unlike other cables commonly found in homes, they are permitted in damp environments, such as basements.
- Clandestine feeder conductors announced like to NM and NMC cables except that UF cables contain a solid plastic cadre and cannot be "rolled" between fingers.
The following NEC regulations apply to Romex conductors:
- They are not permitted in residential structure higher than three stories, or in any commercial construction.
- They must be protected, secured and clamped to device boxes, junction boxes and fixtures.
- Support devices that may impairment the cables, such every bit bent nails and overdriven staples, are not permitted.
- NM and NMC cables should be secured at intervals that do not exceed 4½ anxiety, and they should be secured within 12 inches of junction boxes and panels to which they are fastened. Cables that do not comply with this rule tin sag and are vulnerable to damage.
- They are intended as permanent wiring in homes and should not be used every bit a substitute for appliance wiring or extension cords.
Note: Some communities take never allowed the utilize of Romex wiring in residential construction. Armored cable is typically used in these communities.
Armored Cables (Air-conditioning)
Armored cablevision (AC), also known as BX, was developed in the early on 1900s by Edwin Greenfield. Information technology was first chosen "BX" to abbreviate "production B – Experimental," although Air conditioning is far more normally used today. Similar Romex cables, they cannot be used in residences higher than three stories, and the rules for protection and support of AC wiring are essentially the same as the rules for Romex. Dissimilar Romex, however, Air conditioning wiring has a flexible metallic sheathing that allows for extra protection. Some major manufacturers of armored cablevision are General Cable, AFC Cable Systems, and United Copper Systems.
Service Entry (SE) Conductors
These cables begin at the splice and enter the meter. They are not permitted inside homes, with the exception of "style R" SE cable that can serve equally interior wiring in branch circuits for ovens and clothes dryers. Style R cables should be clearly marked on their jacket surfaces.
Knob-and-Tube (KT) Wiring
Most houses synthetic prior to World War II were wired using the knob-and-tube method, a system that is now obsolete. They are more hard to improve than modern wiring systems and are a fire hazard. Knob-and-tube wiring is supported with ceramic knobs, and runs intermittently though ceramic tubes below framing and at locations where the wires intersect. Whenever an inspector encounters knob-and-tube wiring, s/he should identify it as a defect and recommend that a qualified electrician evaluate the organization. The following are a few reasons why inspectors should be wary of this one-time wiring system:
- The dissipated oestrus from knob-and-tube wiring can pose a fire hazard if the wires are enveloped in building insulation. A possible exception is fiberglass insulation, which is fire-resistant, although fifty-fifty this blazon of insulation should not cover knob-and-tube wiring. The homeowner or an electrician should carefully remove any insulation that is constitute surrounding KT wires.
- Knob-and-tube wiring is more than vulnerable to impairment than modern wiring considering it is insulated with fiber materials and varnish, which can become brittle.
- Some insurance companies refuse to write fire insurance for houses with this type of wiring, although this may exist remedied if an electrician can verify that the system is safe.
- Disregarding any inherent inadequacies, existing KT cablevision systems are likely to be dangerous because they are almost guaranteed to be at least fifty years former.
In summary, inspectors should understand the different types of conductors that are commonly found in homes.
How Many Wires For Ac Underground Service,
Source: https://www.nachi.org/conductor-types.htm
Posted by: echolsnotake.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Many Wires For Ac Underground Service"
Post a Comment